Table of Contents
Image formation by concave and convex mirror when the object placed at different locations
Concave mirror image formation | characteristics of image formed by concave mirror and concave mirror | Image formation by concave and convex mirror CBSE notes for class 10
The image formed by the concave & convex mirror is a very important topic for the students of 10th standard. Therefore, it is very important to know the terminology used in spherical mirrors before knowing how the image is formed from concave and convex mirrors.
So, here is some basic terminologies that are used in image formation by the concave and convex mirror.
Terms Related to Spherical Mirror (Concave & Convex)
1. Centre of curvature (C):-
The center of curvature of the mirror is the center of the spherical shell from where the spherical mirrors are formed by cutting the circular cross-section of the spherical shell. The center of curvature is usually denoted by “C”.

2. Radius of curvature (R):-
The radius of a spherical shell from which the mirror is curved called the radius of curvature. OR
It is the linear distance between the center of curvature (C) and the pole (P). It is usually denoted by “R”.
3. Pole (P):-
The central or midpoint of the curved reflecting surfaces of the mirrors is called the pole of the mirror. The “P” symbol is used to represent the pole of the mirror.
4. Principal axis:-
The imaginary line which passes through the pole and center of curvature is called the Principal axis. OR
It is a straight imaginary line that connects to the center of curvature and pole.
5. Aperture:-
Aperture is the diameter of the reflecting surfaces of the mirror. Or simply you can say the part of the mirror which is exposed to the incident light.
6. Principal Focus or Focus point (F):-
The rays which are coming parallel to the principal axis and after reflection from the reflecting surfaces meet at a point or appear to meet at a point on the principal axis is called the principal focus. It is usually denoted by the letter F.
7. Focal length (f):-
It is the linear distance between the pole (P) and the principal focus (F) of the spherical mirror.
So, by knowing these basic terms, which are related to spherical mirrors, you will be able to understand the image formation of mirrors.
Image formation by Spherical mirrors:-
Here we will see how an image is formed by placing the object in different positions in front of a convex and concave mirror. In addition, we will also discuss the following conditions.
A.) What will be the nature and size of the image formed by spherical mirrors?
B.) At what position image will form from the pole of the mirror?
Image formed by concave mirror and convex mirror:-
For image formation, one has to focus only on two to three rays that come from the object.
1.) The first rays come parallel to the principal axis and after reflection, the rays cut the axis on the principal axis i.e. focus.
2.) The second light ray will be that which passes through the center of curvature.
3.) The third light ray will be the one that passes through the focus and becomes parallel after reflection.
Image formation for concave mirror
Condition 1:- Image formed by concave mirror when object placed at infinity
Considering the light rays coming from an object placed at infinity to the reflecting surface MM’. Let the pole of reflecting surface is P, the center of curvature is C and the principal focus is F.

| Ray diagram of concave mirror when the object is put at infinity | |
| Position of an object (u) | At infinity |
| Position of image formed (v) | At Focus (F) |
| Nature of the Image | Real and Inverted |
| Size of Image | Point like image (Highly Diminished) |
Condition 2:- Image formed by concave mirror when the object is beyond the center of curvature (C)
As you can see in the figure that object AB is placed at B beyond C. In addition, the image A’B’ is constructed at point B’ between C and F.

| Ray diagram of concave mirror when object put beyond the center of curvature | |
| Position of an object (u) | Beyond center of curvature C |
| Position of image formed (v) | Between Center of curvature (C) and focus (F) |
| Nature of the Image | Real and Inverted |
| Size of Image | Small or Diminished |
Condition 3:- Image formed by concave mirror when the object is placed at center of curvature (C)
In the given figure you can see the object AB is placed at the center of curvature C. Equal and inverted image A’B’ is formed at C.
| Ray diagram of concave mirror when object at Center of curvature C | |
| Position of an object (u) | At the center of curvature C |
| Position of image formed (v) | At the center of curvature C |
| Nature of the Image | Real and Inverted |
| Size of Image | Equal to the size of object (Same size) |
Condition 4:- Image formed by concave mirror when the object is placed between center of curvature (C) and principal focus(F)
In that given image, you can see the object is placed between the center of curvature (C) and focus (F).
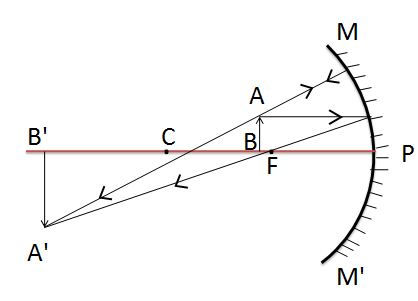
| Ray diagram of concave mirror when the object is put beyond C | |
| Position of an object (u) | Between the center of curvature C & focus (F) |
| Position of image formed (v) | Beyond the center of curvature C |
| Nature of the Image | Real and Inverted |
| Size of Image | Enlarged or Magnified |
Condition 5:- Image formation by concave mirror when the object is placed at principal focus(F)
In that case, object AB is placed at focus F and the image A’B’ forms at infinity.

| Ray diagram of concave mirror when the object is put at principal focus F | |
| Position of an object (u) | At the principal focus F |
| Position of image formed (v) | At infinity |
| Nature of the Image | Real and Inverted |
| Size of Image | Highly Magnified |
Condition 6:- Image formation by concave mirror when the object is placed between pole P and the principal focus(F)
In that figure, the object AB is placed between the pole and focus. The image of the object is formed behind the mirror which is magnified.
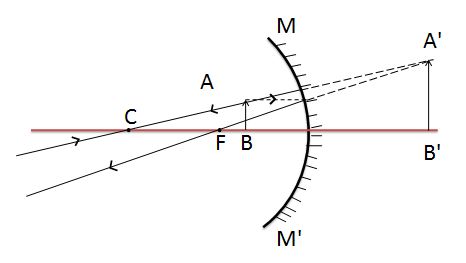
| Ray diagram of concave mirror when object put between the pole and focus | |
| Position of an object (u) | Between pole and principal focus |
| Position of image formed (v) | Behind the mirror |
| Nature of the Image | Virtual and erect |
| Size of Image | Magnified (enlarged) |
Read that: Ohms law
Image formation for convex mirror
Condition 1:- Image formed by convex mirror when the object is placed at infinity
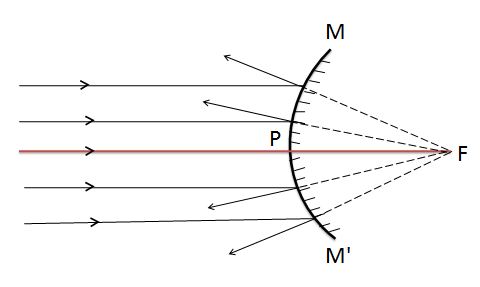
| Ray diagram of convex mirror when object put at infinity | |
| Position of an object (u) | At infinity |
| Position of image formed (v) | At focus behind the mirror |
| Nature of the Image | Virtual and erect |
| Size of Image | Point like (highly diminished) |
Condition 2:- Image formed by convex mirror when the object is placed between the pole P and infinity
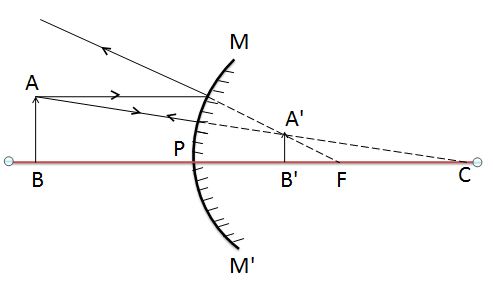
| Ray diagram of convex mirror when object put between the pole and infinity | |
| Position of an object (u) | Between the pole and infinity |
| Position of image formed (v) | Between pole and focus behind the mirror |
| Nature of the Image | Virtual and erect |
| Size of Image | Small (diminished) |
Image formation tabular data for concave mirror in a short form:-
In this table, the image formed by a concave mirror is given while placing the object in a different location.
| Position of an object (u) | Position of the image (v) | Nature of the image | Size of image formed by concave |
| At infinite | At Focus (F) | Real & inverted | Highly Diminished (Point Like) |
| Beyond Center of curvature (C) | Between C and F | Real & inverted | Diminished (Small) |
| At Center of curvature (C) | At Center of curvature (C) | Real & inverted | Same size as object |
| Between C and F | Beyond C | Real & inverted | Magnified (Enlarge) |
| At principal focus F | At infinity | Real & inverted | Highly Magnified |
| Between Pole and Focus | Behind the mirror | Virtual and Erect | Magnified (Enlarge) |
Image formation tabular data for convex mirror in a short form:-
This table contains the details of the image formed by a convex mirror while placing the object in a different location.
| Position of an object (u) | Position of the image (v) | Nature of the image | Size of image formed by concave |
| At infinite | At Focus (F) behind the mirror | virtual and Erect | Highly Diminished (Point Like) |
| Between Pole P and Infinity | between pole and focus behind the mirror | Virtual and Erect | Diminished (Small) |
Conclusion:-
From the point of view of the class 10th board, this topic of a spherical mirror is very important. If you know how to draw a ray diagram for concave and convex mirrors, you will be able to create an image. I hope you will understand the given notes of the image formation by concave and convex mirrors. But still, if there is any doubt related to this topic, then definitely ask in the comment box.
